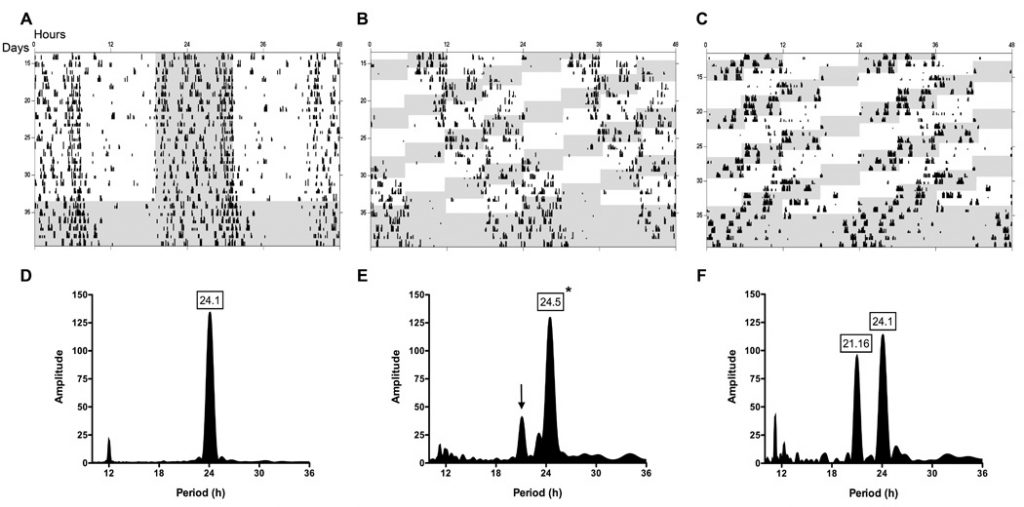
Prolonged subjection to unstable work or lighting schedules, significantly in rotating shift-workers, is related to an elevated danger of immune-related ailments, together with a number of cancers.
Consequences of continual circadian disruption may lengthen to the innate immune system to advertise cancer growth, as NK cell operate is modulated by circadian mechanisms and performs a key function in lysis of tumor cells. To decide if NK cell operate is disrupted by a mannequin of human shift-work and jet-lag, Fischer (344) rats have been uncovered to both a normal 12:12 light-dark cycle or a continual shift-lag paradigm consisting of 10 repeated 6-h photic advances occurring each 2 d, adopted by 5-7 d of fixed darkness.
This mannequin resulted in appreciable circadian disruption, as assessed by circadian running-wheel exercise. NK cells have been enriched from management and shifted animals, and gene, protein, and cytolytic exercise assays have been carried out. Chronic shift-lag altered the circadian expression of clock genes, Per2 and Bmal1, and cytolytic elements, perforin and granzyme B, in addition to the cytokine, IFN-γ. These alterations have been correlated with suppressed circadian expression of NK cytolytic exercise.
Further, continual shift-lag attenuated NK cell cytolytic exercise beneath stimulated in vivo circumstances, and promoted lung tumor growth following i.v. injection of MADB106 tumor cells. Together, these findings counsel continual circadian disruption promotes tumor growth by altering the circadian rhythms of NK cell operate.
Natural killer (NK) cells are a heterogeneous inhabitants of innate lymphocytes whose potent anticancer properties make them superb candidates for mobile therapeutic utility. However, our lack of understanding of the function of NK cell variety in antitumor responses has hindered advances in this space.
In this examine, we describe a brand new CD56dim NK cell subset characterised by the lack of expression of DNAX accent molecule-1 (DNAM-1). Compared with CD56shiny and CD56dimDNAM-1pos NK cell subsets, CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cells displayed diminished motility, poor proliferation, decrease manufacturing of interferon-γ, and restricted killing capacities.
Soluble elements secreted by CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cells impaired CD56dimDNAM-1pos NK cell-mediated killing, indicating a possible inhibitory function for the CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cell subset. Transcriptome evaluation revealed that CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cells represent a brand new mature NK cell subset with a selected gene signature.
Upon in vitro cytokine stimulation, CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cells have been discovered to distinguish from CD56dimDNAM-1pos NK cells. Finally, we report a dysregulation of NK cell subsets in the blood of sufferers identified with Hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse massive B-cell lymphoma, characterised by decreased CD56dimDNAM-1pos/CD56dimDNAM-1neg NK cell ratios and diminished cytotoxic exercise of CD56dimDNAM-1pos NK cells. Altogether, our knowledge provide a greater understanding of human peripheral blood NK cell populations and have vital scientific implications for the design of NK cell-targeting therapies.
NKp44 is a receptor encoded by the NCR2 gene, which is expressed by cytokine-activated pure killer (NK) cells which are concerned in anti-AML immunity. NKp44 has three splice variants similar to NKp44ITIM+ (NKp44-1) and NKp44ITIM- (NKp44-2, and NKp44-3) isoforms. RNAseq knowledge of AML sufferers revealed related survival of NKp46+NKp44+ and NKp46+NKp44- sufferers.
However, if grouped in response to the NKp44 splice variant profile, NKp44-1 expression was considerably related to poor survival of AML sufferers. Moreover, activation of PBMC from wholesome controls confirmed co-dominant expression of NKp44-1 and NKp44-3, whereas major NK clones present extra numerous NKp44 splice variant profiles. Cultured major NK cells resulted in NKp44-1 dominance and impaired operate related to PCNA over-expression by goal cells.
This impaired useful phenotype may very well be rescued by blocking of NKp44 receptor. Human NK cell traces revealed co-dominant expression of NKp44-1 and NKp44-3 and confirmed a useful phenotype that was not inhibited by PCNA over-expression.
Furthermore, transfection-based overexpression of NKp44-1, however not NKp44-2/NKp44-3, reversed the endogenous resistance of NK-92 cells to PCNA-mediated inhibition, and resulted in poor formation of secure lytic immune synapses. This analysis contributes to the understanding of AML prognosis by shedding new gentle on the useful implications of differential splicing of NKp44.
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphoid cells vital for host protection in opposition to pathogens and mediate antitumor immunity. Cytokine receptors transduce vital alerts that regulate proliferation, survival, activation standing, and set off effector features.
Here, we overview the roles of main cytokines that regulate human NK cell growth, survival, and operate, together with IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, and IL-21, and their translation to the clinic as immunotherapy brokers. We spotlight a current growth in NK cell biology, the identification of innate NK cell reminiscence, and concentrate on cytokine-induced memory-like (CIML) NK cells that end result from a short, mixed activation with IL-12, IL-15, and IL-18.
This activation outcomes in lengthy lived NK cells that exhibit enhanced performance once they encounter a secondary stimulation and gives a brand new method to allow NK cells for enhanced responsiveness to an infection and cancer.
An improved understanding of the mobile and molecular points of cytokine-cytokine receptor alerts has led to a resurgence of curiosity in the scientific use of cytokines that maintain and/or activate NK cell antitumor potential. In the future, such methods shall be mixed with unfavourable regulatory sign blockade and enhanced recognition to comprehensively improve NK cells for immunotherapy.
Dopaminergic Regulation of Innate Immunity: a Review
Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter in the central nervous system in addition to in peripheral tissues. Emerging proof nonetheless factors to DA additionally as a key transmitter between the nervous system and the immune system in addition to a mediator produced and launched by immune cells themselves.
Dopaminergic pathways have obtained to date intensive consideration in the adaptive department of the immune system, the place they play a job in well being and illness reminiscent of a number of sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and Parkinson’s illness.
Comparatively little is thought about DA and the innate immune response, though DA might have an effect on innate immune system cells reminiscent of dendritic cells, macrophages, microglia, and neutrophils. The current overview goals at offering an entire and exhaustive abstract of at the moment out there proof about DA and innate immunity, and to grow to be a reference for anybody doubtlessly in the fields of immunology, neurosciences and pharmacology.
A wide selection of dopaminergic medication is used in therapeutics for non-immune indications, reminiscent of Parkinson’s illness, hyperprolactinemia, shock, hypertension, with a normally favorable therapeutic index, and they is perhaps comparatively simply repurposed for immune-mediated illness, thus resulting in progressive therapies at low worth, with profit for sufferers in addition to for the healthcare methods.
Neonatal Natural Killer (NK) cells present useful impairment and enlargement of a CD56 unfavourable inhabitants of unsure significance.NK cells have been remoted from twine blood and from grownup donors. NK subpopulations have been recognized as optimistic or unfavourable for the expression of CD56 and characterised for expression of granzyme B and floor markers by multi-parameter circulate cytometry. Cell operate was assessed by viral suppression and cytokine manufacturing utilizing autologous lymphocytes contaminated with HIV.
Activating (NKp30, NKp46) and inhibitory (Siglec-7) markers in wholesome infants and adults have been in contrast with viremic HIV-infected adults.Cord blood contained elevated frequencies of CD56 unfavourable (CD56neg) NK cells with diminished expression of granzyme B and diminished manufacturing of IFNγ and the CC-class chemokines RANTES, MIP1α and MIP1β upon stimulation.
Both CD56pos and CD56neg NK subpopulations confirmed impaired viral suppression in twine blood, with impairment most marked in the CD56neg subset. CD56neg NK cells from twine blood and HIV-infected adults shared decreased inhibitory and activating receptor expression compared with CD56pos cells.CD56neg NK cells are elevated in quantity in regular infants and these effectors present diminished anti-viral exercise.
Like the expanded CD56neg inhabitants described in HIV-infected adults, these NK cells display useful impairments which can replicate insufficient growth or activation.
