Natural killer (NK) cells are essential regulators of antiviral and anti-tumor immune responses. Although in people some NK cell transcriptional packages are comparatively well-established, NK cell transcriptional networks in non-human primates (NHP) stay poorly delineated.
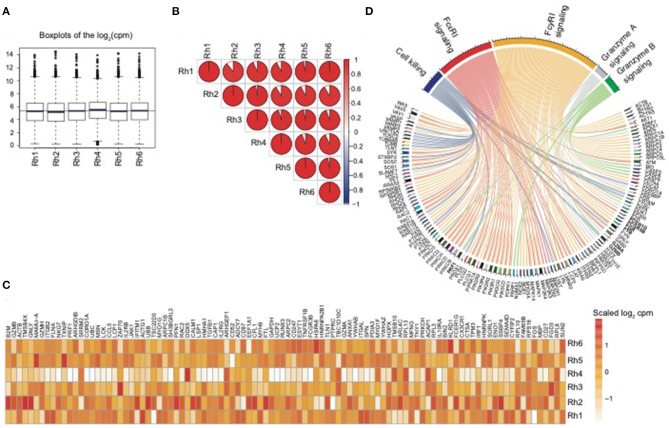
Here we carried out RNA-Seq experiments utilizing purified NK cells from experimentally naïve rhesus macaques, offering the first transcriptional characterization of pure NK cells in any NHP species. This novel NK cell transcriptomic signature (NK RMtsig) overlaps with revealed human NK signatures, permitting us to establish new key signaling and transcription issue networks underlying NK cell operate.
Finally, we present that making use of NK RMtsig to an unrelated rhesus macaque cohort contaminated with SIVmac251 or ZIKV can sensitively detect NK cell repertoire perturbations, thus confirming applicability of this strategy. In sum, we suggest this NHP NK cell signature will function a helpful useful resource for future research involving an infection, illness or remedy modalities in NHP.
Enhancing community activation in pure killer cells: predictions from in silico modeling.
Natural killer (NK) cells are half of the innate immune system and are succesful of killing diseased cells. As a consequence, NK cells are getting used for adoptive cell therapies for most cancers sufferers.
The activation of NK cell stimulatory receptors results in a cascade of intracellular phosphorylation reactions, which prompts key signaling species that facilitate the secretion of cytolytic molecules required for cell killing. Strategies that maximize the activation of such intracellular species can enhance the chance of NK cell killing upon contact with a most cancers cell and thereby enhance efficacy of NK cell-based therapies.
However, resulting from the complexity of intracellular signaling, it’s troublesome to infer a priori which methods can improve species activation. Therefore, we constructed a mechanistic mannequin of the CD16, 2B4 and NKG2D signaling pathways in NK cells to simulate methods that improve signaling.
The mannequin predictions had been match to revealed knowledge and validated with a separate dataset. Model simulations show robust community activation when the CD16 pathway is stimulated. The magnitude of species activation is most delicate to the receptor’s preliminary focus and the price at which the receptor is activated.
Co-stimulation of CD16 and NKG2D in silico required fewer ligands to attain half-maximal activation than different combos, suggesting co-stimulating these pathways is handiest in activating the species. We utilized the mannequin to foretell the results of perturbing the signaling community and discovered two methods that may potently improve community activation.
When the availability of ligands is low, it’s extra influential to engineer NK cell receptors which can be immune to proteolytic cleavage. In distinction, for top ligand concentrations, inhibiting phosphatase exercise results in sustained species activation. The work offered right here establishes a framework for understanding the advanced, nonlinear facets of NK cell signaling and supplies detailed methods for enhancing NK cell activation.
